T4K3.news
Psychedelics map reveals broad brain targets
A study profiles 41 psychedelics across 318 receptors, showing broad receptor engagement beyond 5HT2A.

A new study maps 41 psychedelic compounds across multiple brain receptors, challenging the idea that effects come only from 5HT2A.
Psychedelics reveal broader brain targets with safety implications
Researchers profiled 41 psychedelic compounds by testing their interactions with 318 G protein coupled receptors, and for LSD, 450 kinases. They began with 255 candidate molecules, used structure similarity to select 31 diverse compounds, and added 10 analogs to cover major chemotypes, creating a 41-molecule dataset. The team then used computational methods to predict targets and validated these predictions with functional assays.
The results show all compounds strongly activate the 5HT2A receptor, but they also engage other serotonin receptors, along with dopamine and adrenergic receptors. Activation of the 5HT2B receptor across all chemical classes raises safety concerns linked to heart valve disease with repeated or long-term use. Dopamine receptor activity is most pronounced with lysergamides like LSD, while adrenergic activity helps explain heightened arousal. The researchers mapped intracellular signaling and found a bias toward G protein pathways through 5HT2A, with variable beta-arrestin recruitment. They compared hallucinogenic and non-hallucinogenic relatives, noting that lisuride is more selective and shows a different signaling profile, which may help explain its lack of perceptual effects.
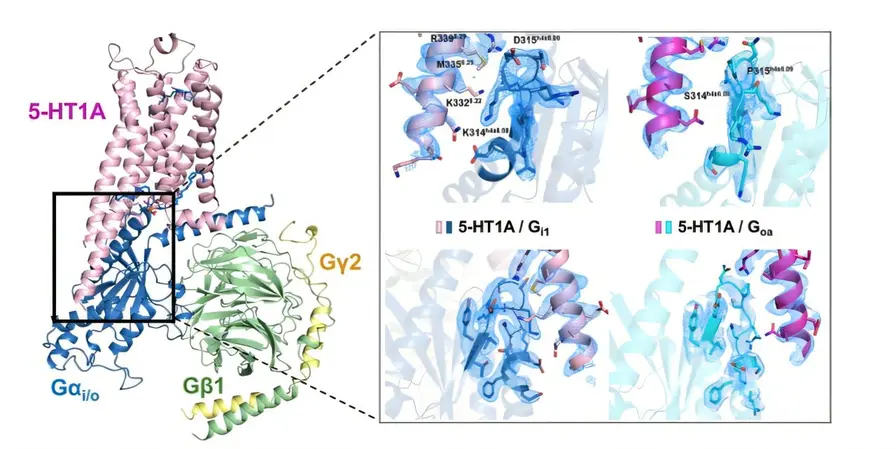
Structural work using cryo-EM showed how LSD binds to the D2 receptor, revealing interactions that stabilize the molecule in a binding pose similar to serotonin receptor complexes. The team also found no direct evidence that psychedelics activate TrkB, suggesting plasticity effects arise indirectly. Behavioral data from animals and dose estimates from human reports linked stronger 5HT2A activation and certain signaling biases to greater hallucinogenic strength and lower human doses, implying lab receptor data can predict some clinical outcomes.
Key Takeaways
"We may need to design more precise, psychedelic-inspired molecules that avoid 5HT2B activation to mitigate cardiac valvulopathy risk."
Jain on safety design implications
"These compounds primarily act via activation of 5HT2A serotonin receptor in the brain, but they also activate several other serotonin, dopamine and adrenergic receptors."
Jain on polypharmacology
"No evidence for direct TrkB activation suggests plasticity is indirect."
Finding about TrkB
"Our dataset highlights many additional analogs that may hold promise for clinical development."
Study authors on resource value
This study shifts thinking from a single target to a network view. The therapeutic potential of psychedelics may hinge on coordinated activation across multiple receptor pathways, not a single receptor. That makes drug design more complex but could also enable finer control over effects and safety.
At the same time, the findings raise regulatory and safety questions. A repeated-use risk tied to 5HT2B activation means developers must prioritize safer molecular designs. The study’s non-neuronal cell models are a reminder that in vivo brain biology adds layers of complexity that still need testing in living systems. The dataset itself is a valuable resource that could accelerate safer psychedelic-inspired therapies if regulators and researchers use it to guide preclinical and clinical work.
Highlights
- Polypharmacology is the rule, not the exception
- 5HT2B activation is a safety red flag that can't be ignored
- A unified dataset changes how we study psychedelics for good
- Therapy may ride on multiple pathways rather than a single target
Safety risks from 5HT2B activation in psychedelics
All 41 compounds tested activated the 5HT2B receptor, signaling a potential risk for heart valve disease with repeated or long-term use. The study calls for designing psychedelics that avoid 5HT2B and for careful regulatory review as clinical development progresses.
The next phase will test whether these insights translate into safer medicines.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

New study reveals secrets of mood regulation receptors

Alzheimer's progression linked to epigenomic breakdown

Brain map reveals full brain activity in decision making

Mouse brain map reveals visceromotor hub
Kidney Proteomics Maps New Targets for CKM health

New depression cell map
New findings on serotonin receptor could reshape mental health treatments
Study reveals genes linked to mental illness activate in fetal stages
