T4K3.news
New study reveals secrets of mood regulation receptors
Research unveils significant insights into the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor's molecular functions.
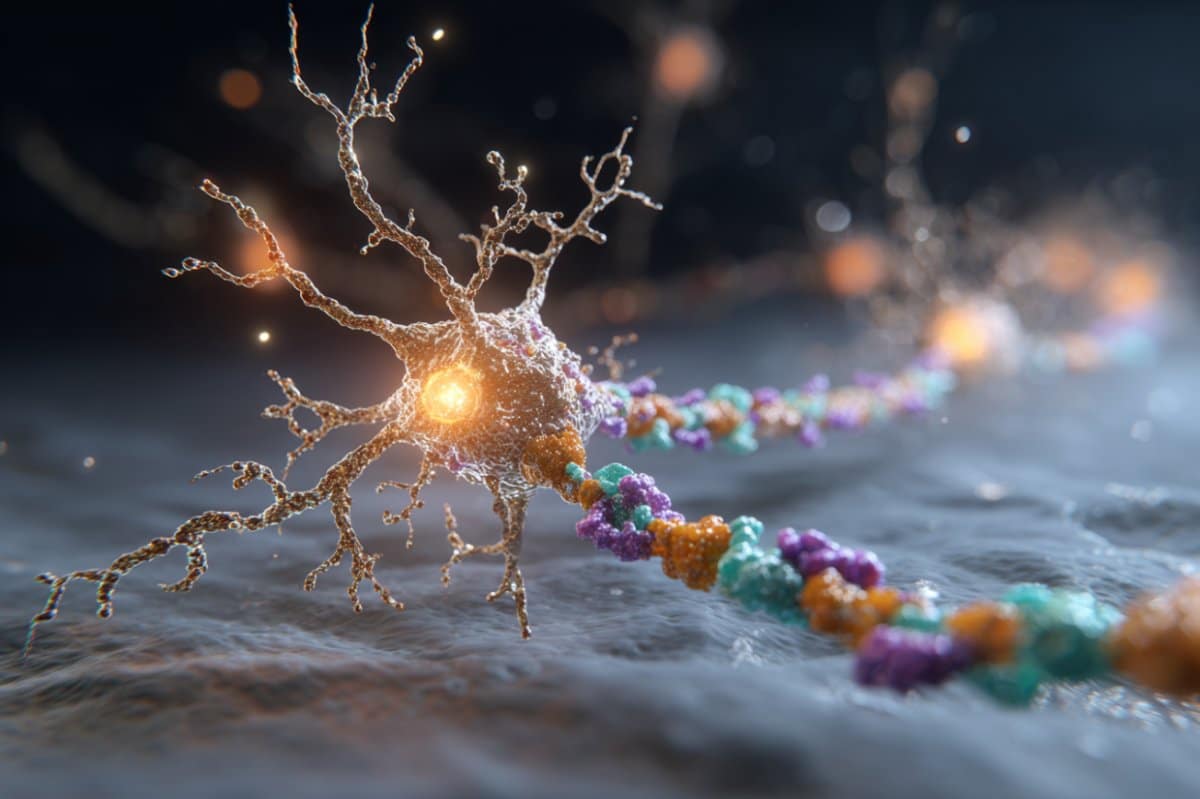

New research illuminates the function of the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor, crucial for mood control.
Research Reveals Mechanism of Serotonin Receptor's Role in Mood Regulation
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have discovered how the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor functions at a molecular level. This receptor is essential for mood regulation and is often targeted by antidepressants and psychedelics. The study, published in Science Advances, indicates that the receptor prefers certain signaling pathways, regardless of the drug used. A phospholipid acts as a crucial helper, guiding the receptor's activity. These findings could lead to improved treatments for conditions like depression and anxiety.
Key Takeaways
"This receptor may help explain why standard antidepressants take long to work."
Dr. Wacker highlights the significance of the 5-HT1A receptor in understanding medication efficacy.
"Our work provides a molecular map of how different drugs ‘push buttons’ on this receptor."
Audrey L. Warren describes the implications of the research for drug design.
This groundbreaking study opens new avenues for understanding mood disorders and the design of psychiatric medications. By identifying the specific pathways activated by the 5-HT1A receptor, researchers can tailor treatments to target specific symptoms, potentially reducing the lengthy wait times typically associated with current antidepressants. The discovery of the phospholipid's influence on receptor behavior suggests a need for more in-depth exploration into the complex mechanisms of brain chemistry.
Highlights
- This research could revolutionize psychiatric treatment.
- A phospholipid works behind the scenes to influence mood regulation.
- Understanding the 5-HT1A receptor opens doors for targeted therapies.
- Faster-acting antidepressants may soon be on the horizon.
Potential for Backlash Against Current Antidepressants
The new findings about the serotonin receptor's functioning may lead to criticism of existing treatments that lack efficacy and speed.
As research progresses, the potential for new treatment pathways shines brightly.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

New findings on serotonin receptor could reshape mental health treatments

New discovery in appetite regulation revealed

New research uncovers gut's role in appetite control
New Research Uncovers Factors Influencing Antidepressant Efficacy

New research links gut bacteria to hunger regulation

Exploring GLP-1 medications and their implications
New insights reveal complexities in dopamine signaling

New study links dieting to worsening depression
