T4K3.news
Surge of hand, foot and mouth disease reported in the US
Health departments confirm rising cases among children, prompting urgent hygiene reminders.
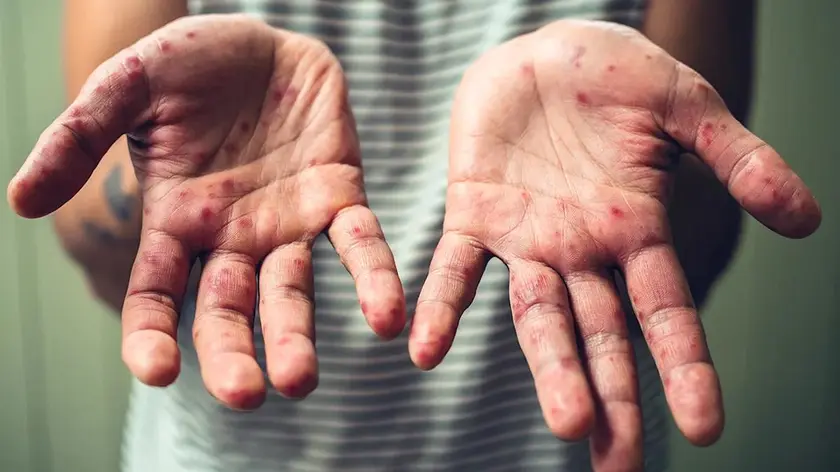

Outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease are increasing among young children in the US.
Surge of hand, foot and mouth disease raises health concerns in the US
Hand, foot and mouth disease is becoming more common in certain U.S. states, with health departments noting significant outbreaks. The illness is especially affecting young children, although anyone can contract it. In Fairfax County, Virginia, six outbreaks have been reported primarily among children under five. The U.S. Virgin Islands have confirmed 189 cases, including a potential fatal instance with a toddler. Experts suggest these outbreaks may often occur during warmer months. Health authorities emphasize the importance of hygiene to reduce transmission, as the disease spreads easily in settings like daycares and schools, particularly during the initial days of illness.
Key Takeaways
"HFMD is a very common infection that is usually mild."
Dr. Tina Q. Tan emphasizes the typical prognosis of HFMD.
"The illness is very contagious, so it can spread quickly in daycare and school settings."
Dr. Tan warns about the rapid transmission of HFMD in communal environments.
"Patients or parents should seek medical care if symptoms worsen."
Dr. Tan advises vigilance in managing worsening symptoms.
"The most common complication of HFMD is dehydration due to painful mouth lesions."
The CDC cites dehydration as a critical risk for those affected.
The increase in hand, foot and mouth disease should alert parents and caregivers, given the contagious nature of the virus. The CDC's emphasis on prevention tactics indicates a proactive stance against further outbreaks. Even mild cases demand careful attention, as complications can arise, creating risks, particularly for infants and young children. As more cases emerge, health officials face the challenge of balancing public safety with the need to keep daycares operational. This situation highlights the fragile nature of public health infrastructures, especially when dealing with preventable childhood diseases.
Highlights
- HFMD spreads quickly in daycares and schools.
- Dehydration from painful mouth sores is a serious concern.
- Public health safety relies on hygiene and awareness.
- No vaccine for HFMD means prevention is key.
Public health risks from HFMD outbreaks pose concerns
Increasing infections of hand, foot and mouth disease among children raise alarms about public health management, especially with serious complications being possible.
Ongoing vigilance and hygiene remain key in combating this contagious virus.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News
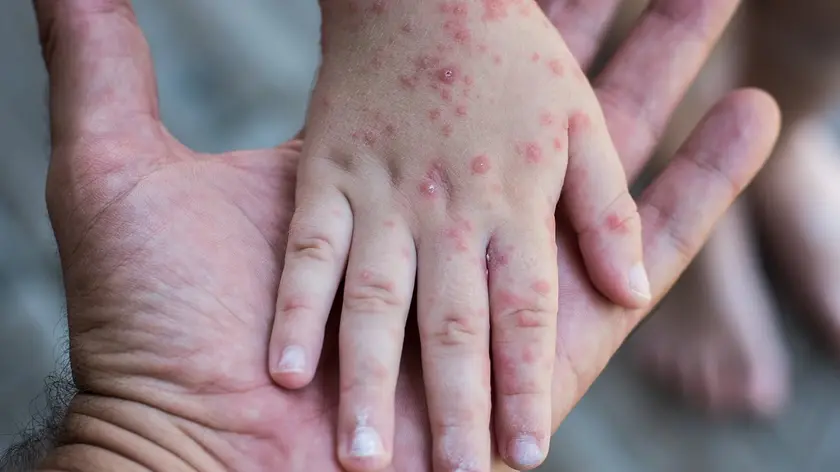
New York City prepares for hand, foot and mouth disease surge

Rising cases of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease reported
Louisiana has the highest STD rate in the U.S.
COVID-19 cases on the rise in Hawaii
Rise in Ritter's disease cases in children at WakeMed

Urgent hepatitis A vaccination advice for Czechia travelers
NHS dentistry under strain

Exploring GLP-1 medications and their implications
