T4K3.news
New research suggests universe may reside in a cosmic void
A study indicates that our universe could be in a vast void, affecting expansion measurements.
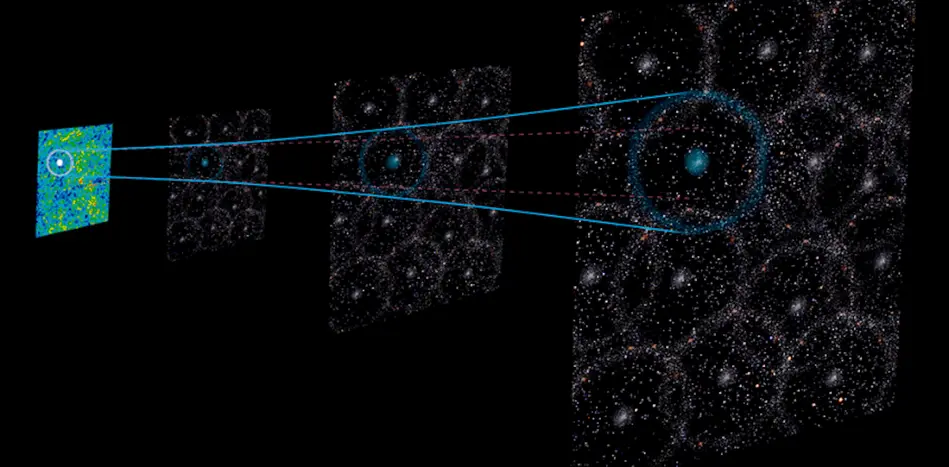
New research suggests our universe may be in a local void with lower matter density.
Living in a giant cosmic void could explain universe's expansion rate
A recent study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society indicates that we might live in a giant cosmic void. This local void is thought to contain about 20% fewer galaxies than average, which may help resolve the Hubble tension. This tension arises from discrepancies in the measured expansion rate of the universe, which is around 10% faster than predictions based on the Lambda-Cold Dark Matter model. The research utilized temperature fluctuations from the cosmic microwave background to understand the structure of the universe better, revealing that our position in a void affects measurements of baryon acoustic oscillations. By comparing BAO measurements from the last two decades, the authors argue that the void model has substantial support, indicating a significantly higher probability than models that assume a uniform density of matter.
Key Takeaways
""Our results suggest that a universe with a local void is about one hundred million times more likely than a cosmos without one.""
This finding highlights the significance of the void model in understanding cosmic expansion.
""This means the likelihood of a universe without a void fitting these data is equivalent to a fair coin landing heads 13 times in a row.""
The comparison emphasizes the improbability of existing models without considering the void.
""By studying CMB temperature fluctuations, we can essentially 'listen' to the sound of the early universe.""
This quote captures the innovative approach to understanding cosmic structure and history.
The implications of this research are profound. If validated, they could reshape our understanding of cosmic structures and how expansion is perceived from different vantage points in the universe. The evidence supporting the void model significantly challenges longstanding cosmological assumptions, suggesting that our neighborhood may be vastly emptier than previously understood. This could also influence future research directions, driving efforts toward more precise measurements to further investigate the universe's actual expansion dynamics. Researchers face the task of reconciling these findings with existing cosmological models or risk an entire paradigm shift in our understanding of cosmic evolution.
Highlights
- Understanding the universe may mean accepting we're in a void.
- If we're in a void, what does that say about cosmic density?
- The universe may be quieter and emptier than we thought.
- Seeing the universe differently could reshape our entire cosmology.
Potential implications for cosmological models
The findings may challenge established theories in cosmology, provoking debate among physicists.
As more data emerges, our cosmic narrative may become clearer than ever before.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

Dark matter may come from a mirror universe

New cosmic discovery reveals larger structures
Astronomers capture first images of cosmic web

New Study Suggests Universe May Be Inside Black Hole

Earendel may be a star cluster not a lone star

Giant meteor impact linked to Grand Canyon landslide

Ancient suns burn anew

Cosmology faces new questions about the Big Bang
