T4K3.news
Interstellar encounter linked to past climate changes
A study ties a past solar system cloud passage to Earth's cooling and climate history.

A past passage through a cold interstellar cloud is linked to Earth’s cooling, backed by isotope records and heliosphere dynamics.
Interstellar Encounter Shaped Earth's Climate
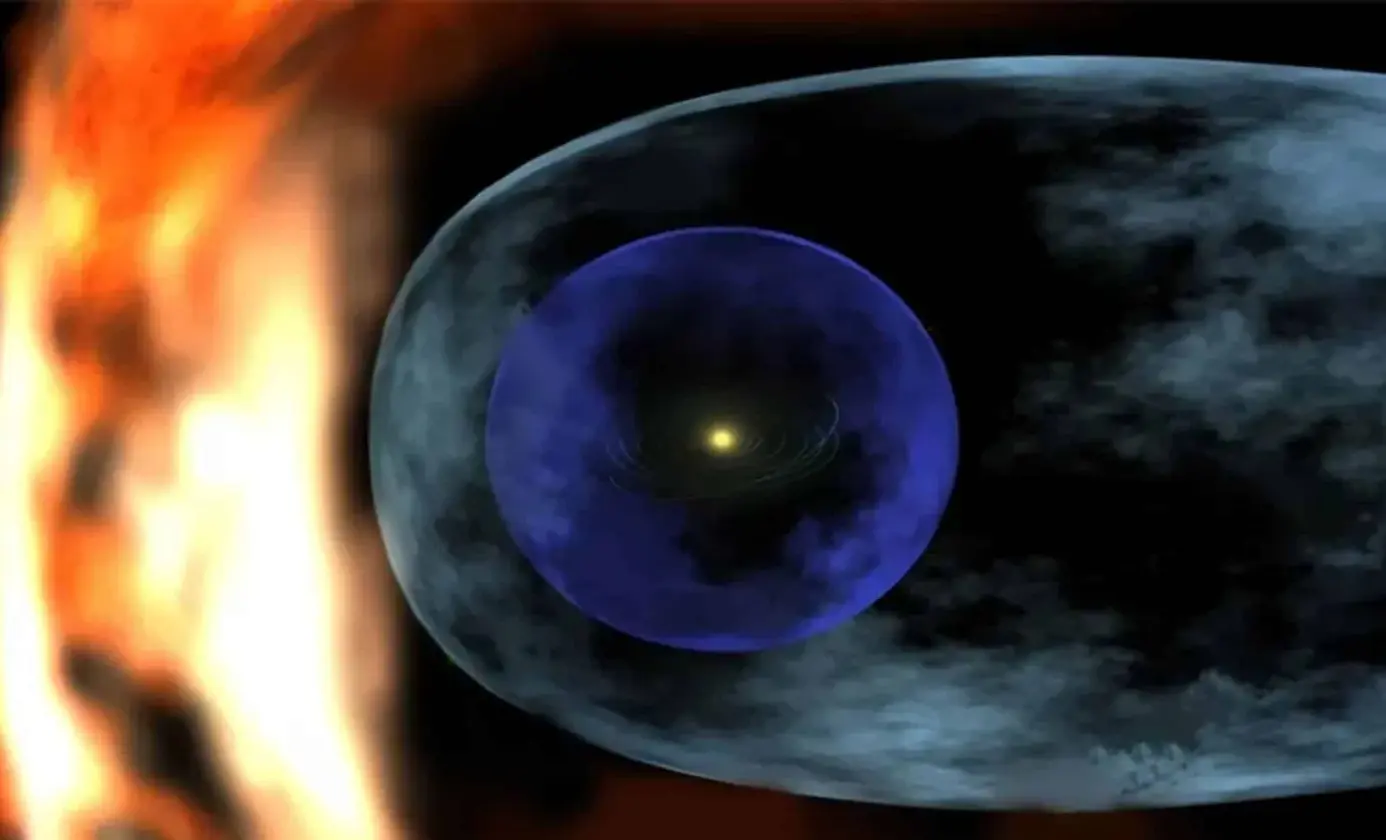
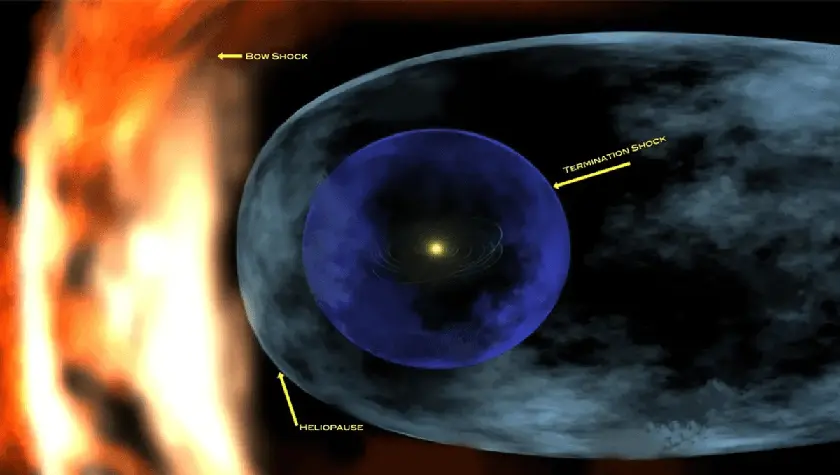
A Nature Astronomy study argues that millions of years ago the Sun and planets moved through a cold, dense interstellar cloud. The contraction of the heliosphere during this passage could have increased exposure to interstellar particles and altered atmospheric chemistry, possibly contributing to cooling and ozone changes. Geological signals, including iron-60 and plutonium-244 found in Antarctic snow and lunar samples, are cited as clues to such an encounter.
The heliosphere acts as a shield against high-energy cosmic radiation and helps protect planets from atmospheric erosion. Today the solar system travels through a relatively sparse region, but a past cloud passage could have produced centuries or even longer effects on climate. Researchers led by Merav Opher say this work is the first to quantify an external solar influence on Earth’s climate, and they note that future encounters with dense interstellar clouds may occur within the next million years as our galaxy changes over time. NASA and space missions continue to map the edge of the solar shield to better understand how such episodes shape planetary environments and the possible trajectory of life.
Key Takeaways
"This paper quantifies an encounter outside the solar system that affected Earth's climate"
Factual note on study’s claim
"The emergence of Homo sapiens was shaped by the need to adapt to climate change"
Observation on human evolution tied to climate
"The heliosphere shields Earth from high energy cosmic radiation"
NASA description of the solar shield
"Once the solar system exited the cloud the heliosphere again fully encompassed Earth"
End of the encounter phase
The idea reframes climate history as a shared story between Earth and its cosmic surroundings. It invites readers to weigh how much past climate shifts might reflect space weather as well as terrestrial factors. It also raises the question of how we tell climate stories when parts of the answer lie beyond our planet.
At the same time, the claim rests on proxies and models that require careful scrutiny. The piece calls for rigorous, cross‑disciplinary work and cautious language to avoid sensationalism as scientists interpret signals from deep time. In short, it asks for humility in science communication while pushing for better measurements of our solar neighborhood and its history.
Highlights
- This paper quantifies an encounter outside the solar system that affected Earth's climate
- The emergence of Homo sapiens was shaped by the need to adapt to climate change
- The heliosphere shields Earth from high energy cosmic radiation
- Once the solar system exited the cloud the heliosphere again fully encompassed Earth
Sensitive topic risk around climate history and cosmic influences
The piece discusses climate change and human evolution in the context of an interstellar event. Presenting this as a direct cause for past climate shifts could mislead readers if not clearly caveated. The article should emphasize uncertainty and reference peer‑reviewed evidence.
Our climate story may have chapters written in the stars, not just in the sea and air.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News
Research suggests interstellar clouds may have cooled Earth

Gulf Stream at Risk

Maine reports first human case of Powassan virus this year

Mysterious blobs under Earth may trigger major volcanic eruptions

Colossal Atlantic white shark spotted off Nantucket

117 Million Year Old Mud Waves Rewrites Atlantic Gateway Timeline
Gulf Stream Nears Tipping Point

Report highlights food crisis impacts on children
