T4K3.news
Study shows handwashing is neglected in hospitals
A University of Surrey study finds nearly half of hospital toilet users skip handwashing.
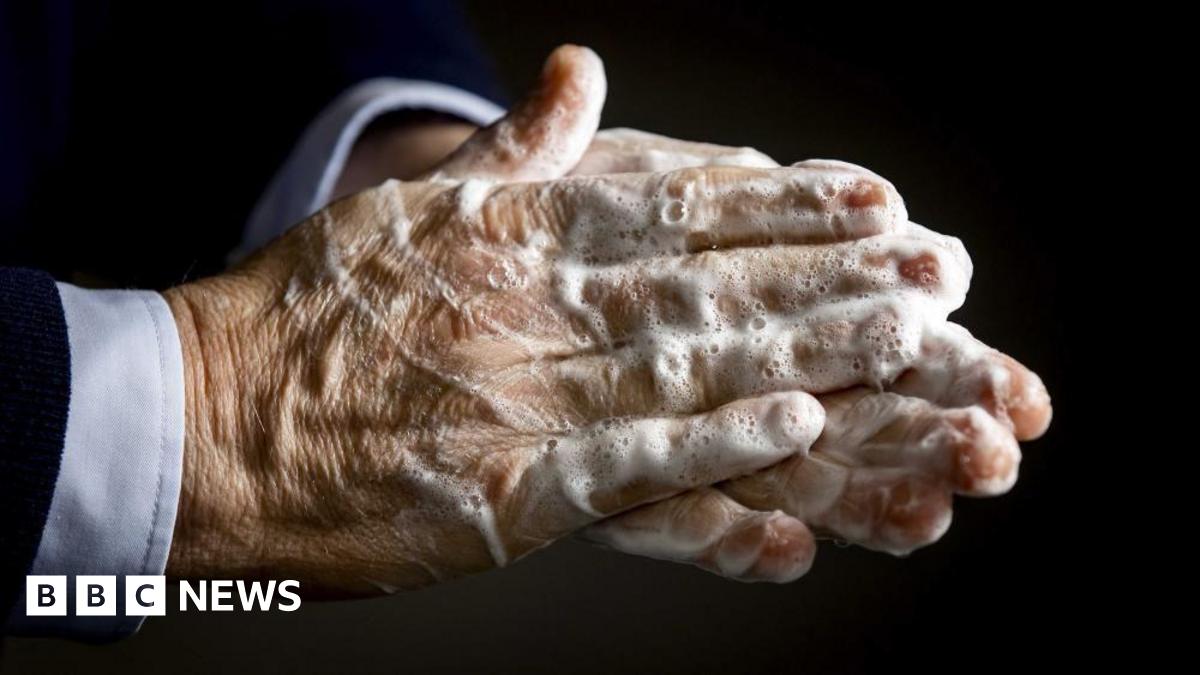

Findings from a recent study reveal troubling hand hygiene practices in hospitals.
Study finds many hospital toilet users bypass handwashing
A study from the University of Surrey shows that nearly half of hospital toilet users do not wash their hands after using the facilities. The research, conducted over 19 weeks in collaboration with Bispebjerg hospital in Denmark, utilized sensors to track hygiene behavior. Out of 2,636 flushes, 43.7% of users skipped handwashing, with some weeks reporting rates as high as 61.8%. Dr Pablo Pereira Doel emphasized that this behavior poses a direct threat to patient safety, challenging the assumption that handwashing habits improved after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Key Takeaways
"This behavior could directly affect patient safety"
Dr Pablo Pereira Doel stresses the importance of handwashing in hospitals
The alarming results of this study highlight a significant gap in hand hygiene compliance, especially in hospital settings where the stakes are high. The fact that such a large percentage of people neglect to wash their hands raises concerns about infection control and overall patient safety. This points to a need for more robust hygiene education and possibly more visible reminders about handwashing in public restrooms. The continuing fight against healthcare-associated infections may rely on changing these ingrained habits.
Highlights
- Hand hygiene habits may need a serious overhaul
- Are we really washing our hands enough?
- Infection risks rise when hygiene is ignored
- Handwashing should be second nature, but it's not
Concerns over hospital hygiene practices
The study reveals low handwashing rates, raising issues around patient safety and infection control in hospitals.
Improving hand hygiene in hospitals is crucial for patient safety and wellbeing.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

Study Shows Handwashing Compliance is Alarmingly Low in Hospitals

Warning issued about bathroom hygiene risks

Study Links PFAS Chemicals to Type 2 Diabetes

Weight regain observed after fat jab treatment ends

Dexter software highlights link between childhood trauma and health risks

Study shows pandemic accelerated brain aging

Experts recommend pneumonia booster for care homes
Study reveals genes linked to mental illness activate in fetal stages
