T4K3.news
Research uncovers potato origins linked to tomatoes
Scientists reveal that potatoes originated from ancient interbreeding with tomatoes.
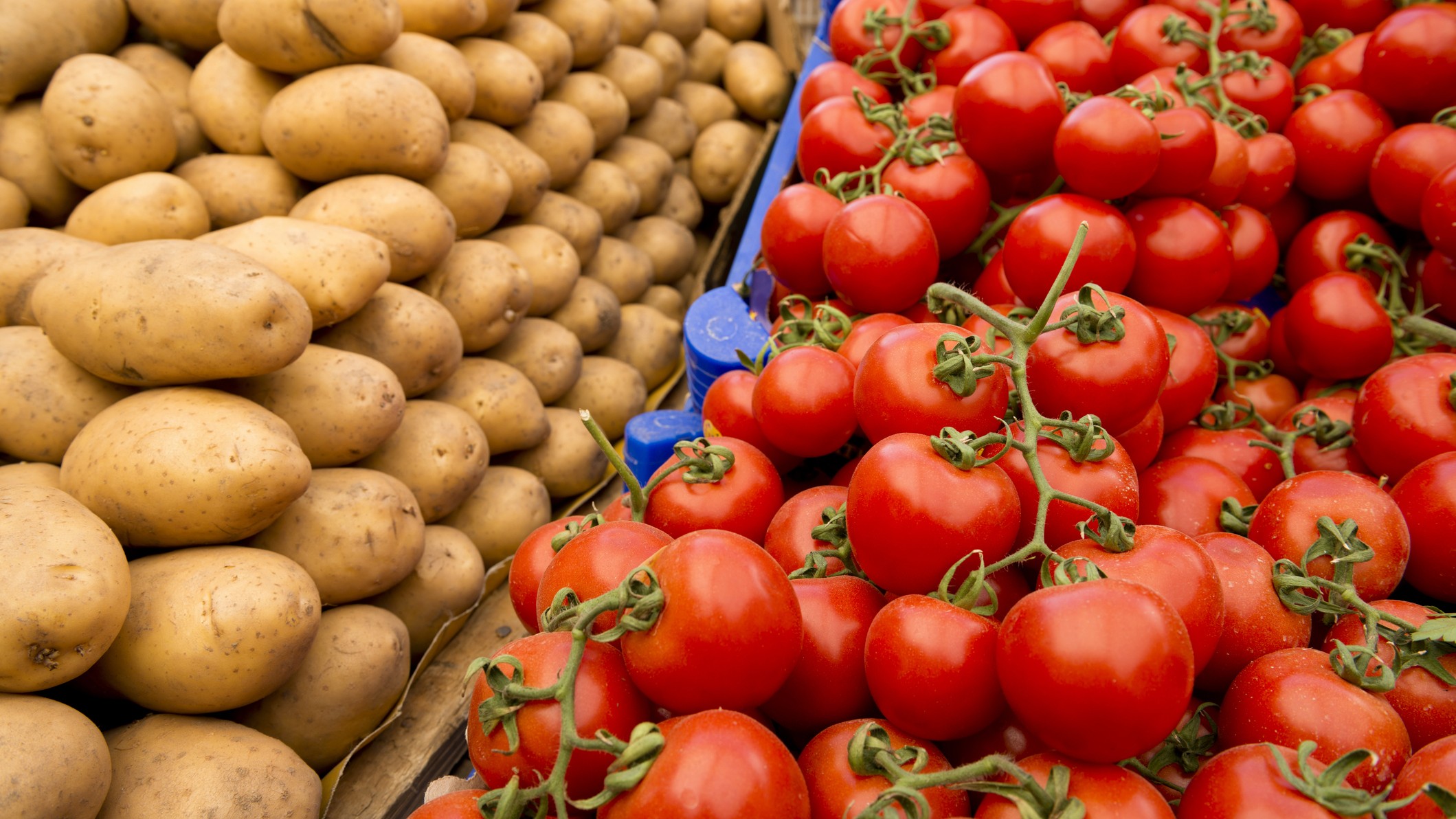

A groundbreaking study uncovers the complex origins of the potato linking it to tomatoes.
New research reveals ancient roots of potatoes from tomatoes
Recent research has traced the origins of the potato to a surprising pairing with wild tomatoes around 8 to 9 million years ago. This discovery stems from scientific analysis that shows cultivated potatoes belong to a lineage called Petota, which emerged from interbreeding between ancestors of tomatoes and another group, Etuberosum. The research team, led by Sandra Knapp from the Natural History Museum in London, analyzed the genomes of various plants to unearth their evolutionary relationships, resulting in insights that explain how hybridization created new traits like tubers. The gene analysis indicates that the potato's ability to store nutrients in tubers allowed it to thrive in diverse environments, promoting its survival and further evolution.
Key Takeaways
"Our findings show how a hybridization event between species can spark the evolution of new traits."
Sanwen Huang emphasizes the role of hybridization in plant evolution.
"Evolving a tuber gave potatoes a huge advantage in harsh environments."
Huang explains how tubers contributed to the adaptability of potatoes.
"From an evolutionary perspective, we had an unresolved disagreement in the relationships between Tomato, Petota and Etuberosum lineages."
Sandra Knapp discusses the significance of the research's findings.
"The new lineage produced tubers, allowing these plants to expand into newly created habitats."
Knapp shares insights on how hybridization allowed for geographical expansion.
This groundbreaking study challenges our understanding of plant evolution, particularly regarding domesticated crops like potatoes. By revealing the genetic connections between tomatoes and potatoes, researchers highlight how hybridization can lead to significant new traits and biodiversity. Understanding this evolutionary history is crucial not only for science but also for agriculture, as it underscores the potential for developing resilient crops in the face of climate change and other challenges. Such insights may lead to greater innovation in food security and agricultural practices, emphasizing the interconnectedness of species in our ecosystem.
Highlights
- From interbreeding, we discovered how new traits emerge.
- Hybridization not only creates new species but enhances resilience.
- The story of potatoes is a complex tale of evolution and survival.
- Understanding plant relationships reshapes our agricultural future.
Potential backlash over agricultural implications
The study's findings may prompt discussions about genetic manipulation practices in agriculture and public perceptions of hybrid crops.
The findings open new avenues for research into crop evolution and resilience.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

Potatoes linked to ancient tomatoes in new research

Study reveals potatoes evolved from tomatoes

Nutrition experts promote affordable superfoods

Fossil Challenges Spiders' Earth Origins
Study Links Gut Health to Chronic Fatigue and Long COVID

Research explains potential eruption links to underground BLOBs
Study reveals genes linked to mental illness activate in fetal stages

Exploring GLP-1 medications and their implications
