T4K3.news
Major Study Identifies Age 50 as Crucial Aging Milestone
Research shows significant acceleration in aging typically begins at age 50, raising health concerns.
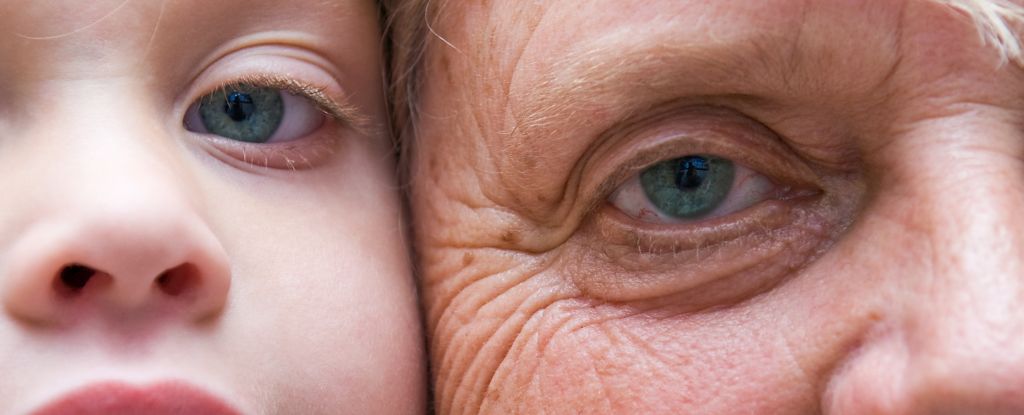

New research shows that aging accelerates significantly around age 50, impacting organ health.
Study Reveals Age 50 as Key Turning Point for Human Aging
A recent study from the Chinese Academy of Sciences finds a significant acceleration in aging that typically begins around age 50. This research involved analyzing proteins in the tissues of 76 organ donors aged 14 to 68. It revealed that organ function declines more steeply after this age, with blood vessels aging rapidly. The findings could lead to better understanding and potential interventions for age-related diseases. The study emphasizes that aging is not a simple, linear process but involves complexities across different body systems, with notable changes between ages 45 and 55.
Key Takeaways
"Our study is poised to construct a comprehensive multi-tissue proteomic atlas spanning 50 years of the entire human aging process."
This quote highlights the intent of the researchers to build a detailed understanding of aging across different tissues over time.
"Based on aging-associated protein changes, we developed tissue-specific proteomic age clocks."
This statement underscores the innovative approach of the study, focusing on how proteins can indicate aging in specific tissues.
"These insights may facilitate the development of targeted interventions for aging and age-related diseases."
This quote reflects the potential practical applications of the research findings in improving health for the aging population.
The implications of this research are profound, suggesting that a targeted approach to health in middle age might be essential. As aging markers rise sharply after age 50, especially in critical organs, preventative measures may become crucial for maintaining health and extending quality of life. This study holds promise for guiding future medical interventions, particularly in cardiovascular health, where aging's impact is pronounced. Understanding when and how our bodies change allows for more informed lifestyle choices and healthcare strategies.
Highlights
- Aging accelerates faster after age 50, impacting health.
- New research shows the complex nature of human aging.
- Understanding aging patterns could lead to better health interventions.
- Age 50 may be the key to understanding organ decline.
Health Risks Linked to Aging Process
The study reveals critical vulnerabilities in organ function as people reach age 50, which may lead to increased healthcare costs and societal implications.
Future research may leverage these findings to enhance health outcomes for older adults.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

Mother identifies rare genetic disorder through global community

Young Americans face higher rectal cancer risk
Link found between sudden diabetes and pancreatic cancer

New research links fat distribution to health risks

Researchers may have found first meteorites from Mercury
Study Links Gut Health to Chronic Fatigue and Long COVID

Experts warn of cancer risks in canned cocktails

Psilocybin Shows Promise in Aging Research
