T4K3.news
Health alert issued after children contract brain-eating parasite
Two children in California were infected by a serious parasite linked to raccoons.

California health officials urge caution after two children contract a serious parasitic infection.
Warnings issued after cases of brain-eating parasite in California
Health officials in California have issued warnings following reports of two children contracting a rare brain-eating parasite known as Baylisascaris procyonis. A 14-year-old boy in Los Angeles was diagnosed in September 2024 and has since made a complete recovery. Tragically, a 15-month-old toddler suffered severe cognitive impairments due to delayed diagnosis. Both boys showed symptoms typical of the infection, including high white blood cell counts and behavioral changes. The CDC's alert emphasizes the need for precaution around raccoons and proper hygiene to prevent such infections, which can be fatal in rare cases. The infection is primarily spread through raccoon feces but may also be transmitted through infected pet dogs.
Key Takeaways
"Young children are at the highest risk of developing a Baylisascaris infection."
This statement underscores the vulnerability of children to zoonotic diseases.
"The infection can cause fatigue, seizures, and potential blindness."
This highlights the serious health consequences associated with B. procyonis infection.
"Health officials urge parents to practice good hygiene and keep children away from raccoons."
This emphasizes the proactive measures recommended to prevent infection.
The cases highlight the growing concern about zoonotic diseases and the risks posed by wildlife in urban areas. With children being particularly vulnerable, the responsibility lies on parents to be vigilant about outdoor play environments, especially where raccoons are prevalent. The fact that the findings prompted intervention from health authorities indicates significant public health implications. Further, the incidents might raise questions about urban wildlife management and community awareness regarding proper sanitation and keeping animals at bay.
Highlights
- Wild animals may pose hidden dangers to our children.
- Knowledge is key in preventing parasitic infections.
- Cities must prioritize safe environments for children.
- When wildlife meets urban life, caution is essential.
Public health concerns surrounding parasitic infection
The recent cases of B. procyonis infections raise significant public health concerns, particularly due to the severe neurological effects on children. Vigilance around raccoon interactions must increase to prevent further infections.
These cases warn about the hidden dangers in urban wildlife interactions.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

Family faces horror after hotel buffet meal in Gran Canaria

Child dies from brain-eating amoeba after swimming in South Carolina lake

Revealing unethical medical experiments

Child dies from brain-eating amoeba in South Carolina

Families overlook key health precautions for summer travel
Confirmed death from brain-eating amoeba in South Carolina
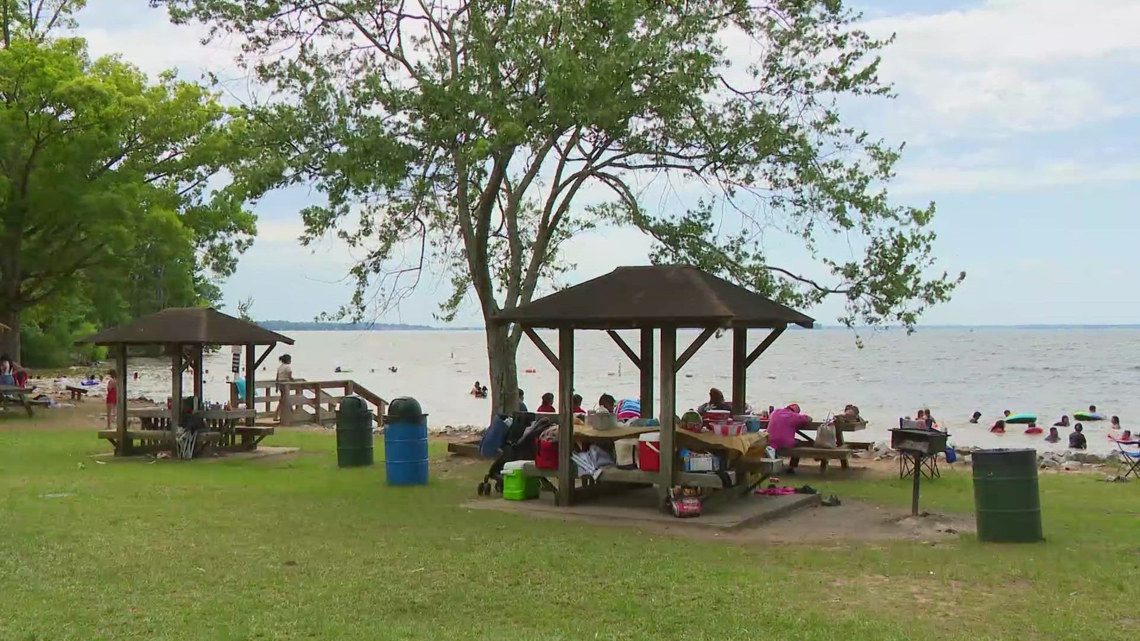

South Carolina confirms death from brain-eating amoeba
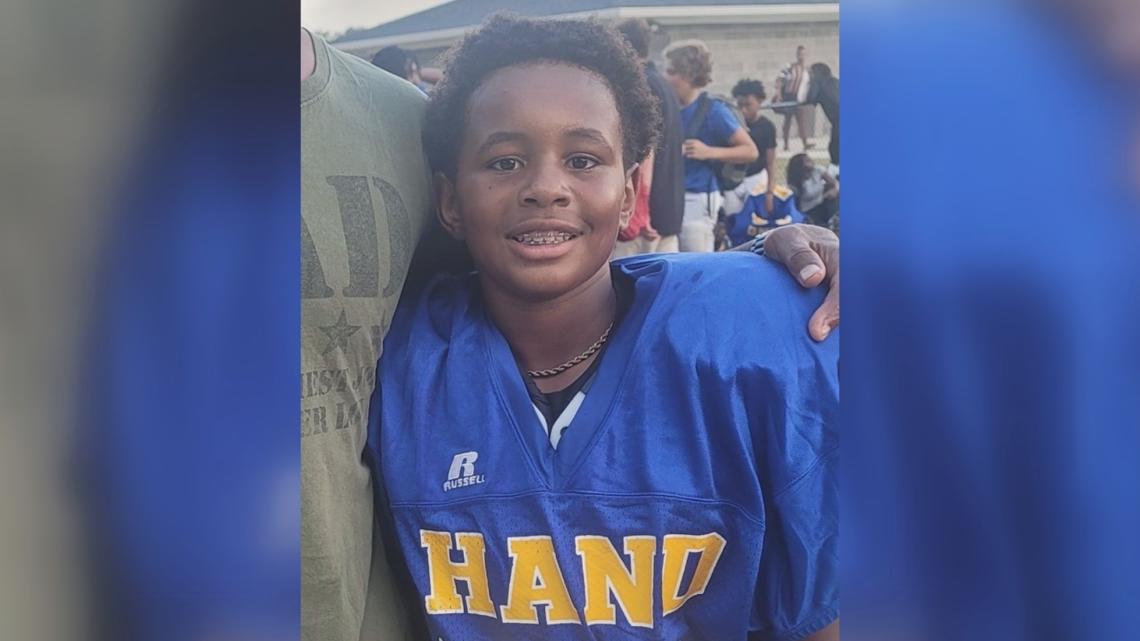

Family of South Carolina child who died from amoeba speaks out
