T4K3.news
Astronomers confirm the universe's earliest black hole
A team has identified a black hole in CAPERS-LRD-z9, dating back 13.3 billion years.
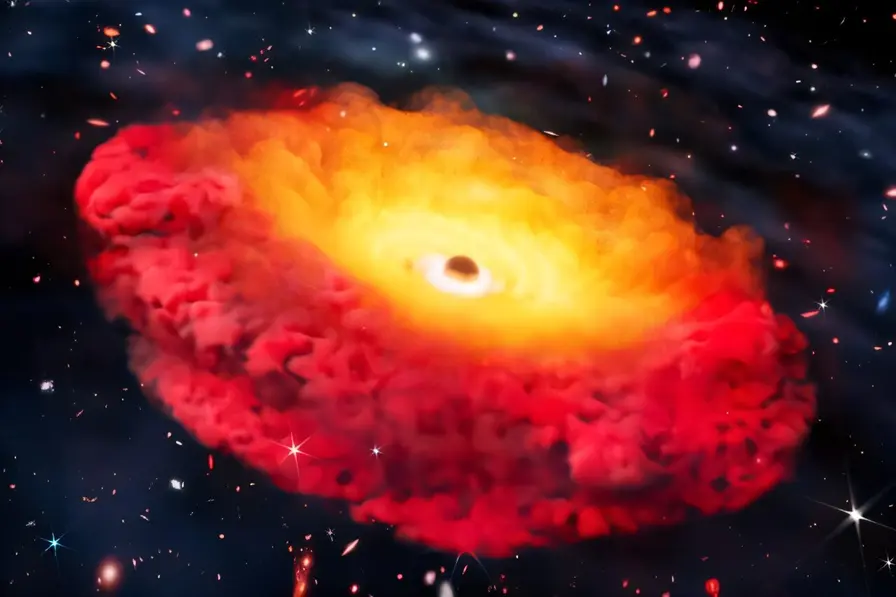

Astronomers have found the most distant confirmed black hole, challenging existing theories.
Discovery of the earliest black hole changes our understanding of the universe
A team from The University of Texas at Austin, working with the Cosmic Frontier Center, has identified the earliest confirmed black hole, located in the galaxy CAPERS-LRD-z9. This black hole emerged just 500 million years after the Big Bang, about 13.3 billion years ago. This discovery offers a window into a foundational period of the universe, pinpointing development stages less understood by scientists. The research appears in The Astrophysical Journal, showcasing the importance of advanced tools like the James Webb Space Telescope, which assisted in characterizing this extraordinary find. The faint galaxy presents a unique signature associated with black holes, prompting astronomers to revisit existing models of cosmic evolution.
Key Takeaways
"This adds to growing evidence that early black holes grew much faster than we thought possible."
This statement emphasizes the surprising growth rate of early black holes, suggesting they may have formed more rapidly than expected.
"When looking for black holes, this is about as far back as you can practically go."
This quote from a lead researcher showcases the groundbreaking nature of the discovery, emphasizing its significance in astronomy.
The discovery of the earliest black hole offers profound implications for cosmology, reshaping how we understand the formation and growth of such massive objects in the universe. Positioned at a time when galaxies were still coalescing, CAPERS-LRD-z9 provides essential evidence that supermassive black holes could form much earlier than previously believed. These findings may lead to reevaluations of the role that black holes played in galaxy formation, suggesting a more interconnected evolution of cosmic structures than thought. As we acquire better observational technology, these revelations will continue to challenge the boundaries of our astronomical knowledge.
Highlights
- A black hole present so early changes everything we know about cosmic evolution.
- This galaxy has the signature that only a black hole can produce.
- The discovery of Little Red Dots was a major surprise from early JWST data.
- Finding this black hole provides evidence that they grew faster than anticipated.
Concerns over funding and research priorities
This discovery raises questions about the allocation of financial resources for astronomical research in the face of budget constraints. Continued funding is crucial for advancing our understanding of the universe, which may be at risk.
Continued research may uncover more about the universe's formative years.
Enjoyed this? Let your friends know!
Related News

JWST finds earliest black hole in the universe

Infinity Galaxy Births a Supermassive Black Hole

James Webb Telescope may have found early cosmic light sources

Astronomers capture first evidence of supermassive black hole formation
Unprecedented Repeating Gamma Ray Burst Detected Beyond the Milky Way

Giant black hole bends light into Einstein ring

Unprecedented Repeating Gamma Ray Burst Defies Explanation
Cosmic Horseshoe Reveals Heaviest Black Hole Yet
